

Jha, Radar Absorbing Materials: From Theory to Design and Characterization, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, MA, 1996.ġ2. Lynch, Jr., D., Introduction to RF Stealth, SciTech Publishing Inc., Raleigh, NC, 2004.ġ1. Air Force Space Surveillance System, System.ġ0. United States Space Surveillance Network. F., Radar Cross Section Measurement, Van Norstrand Reinhold, New York, 1993.ħ. Best strategy for satellite self-defense is orbit change.Ĥ. Such inflated device is susceptible to space debris damage and cumbersome to operate, and may interfere with the original mission of the satellite.
When it is slant illuminated, the RCS of the stealth satellite shows no RCS reduction effects. Results indicate this shape is advantageous in bore sight monostatic backscatter RCS reduction, but in other directions the RCS increases due to sheer size effect, which makes it even more vulnerable to bi-static radar tracking. In this study we examine the RCS of this so-called stealth satellite in S-band with FDTD simulations, and analyze its frequency and radar incident angle dependence.
The most notable RF stealth suggestion among them is the proposal of using an inflatable polymer cone to change its shape and reduce satellite's RCS. To avoid detection, several suggestions have been made in the past to deflect ambient light and decrease the RCS (radar cross section) to avoid detection.

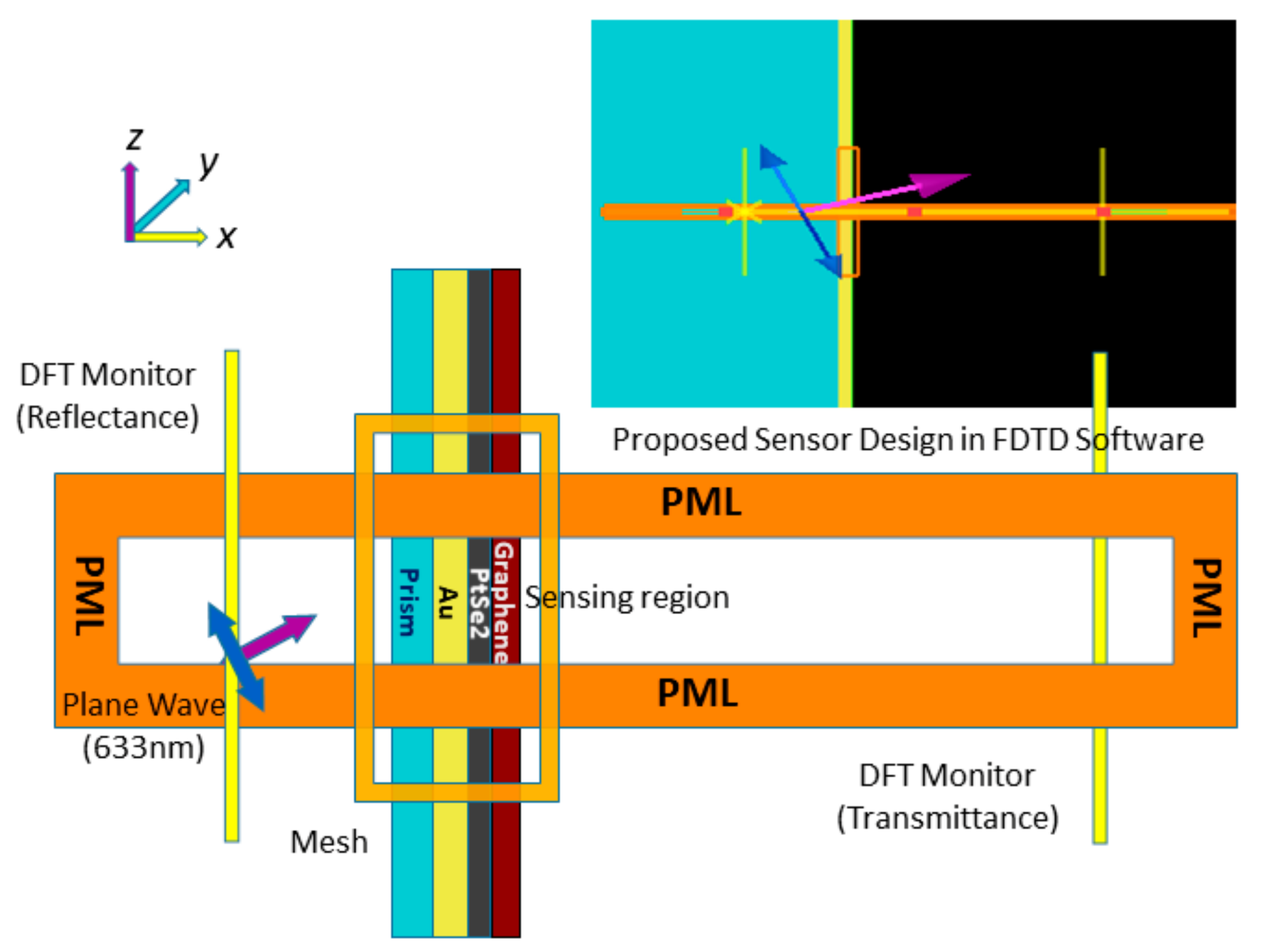
The vulnerability of satellite depends highly on its probability of being detected and tracked, and optics or radars are the two major means of detection. Satellites are the most important link in today's battle field, and with the advancement of anti-satellite technologies like anti-satellite missiles and directed energy weapons, satellites are becoming vulnerable to attack.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
